Spinal Navigation
What is Spinal Navigation?
Spinal navigation, also known as image-guided surgery or computer-assisted navigation, is a cutting-edge technology used in spinal procedures. The patient’s spine is virtually mapped using 3D mapping and real-time imaging. During surgery, surgeons use this map as a precise guide to increase precision and lower risks. Benefits of spinal navigation include reduced radiation exposure, better surgical planning, and elevated safety. It is changing the way that spine surgery is performed by giving surgeons the essential tools they need to provide their patients with the greatest possible results.
Our Approach to Spinal Navigation
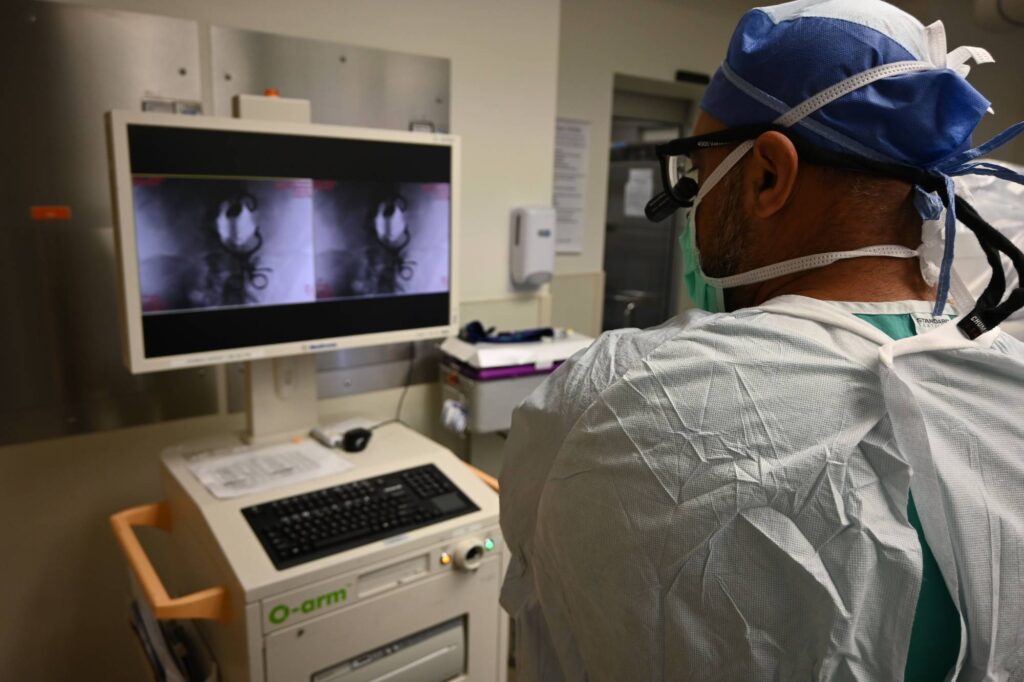
The O-armTM system is a complete multidimensional surgical imaging system that is designed to meet the workflow demands of the surgical environment. Along with StealthStation™ navigation, the O-arm™ system provides enhanced 3D visibility and surgical feedback. The field of spine surgery has been completely transformed by the use of spinal navigation. In order to produce a real-time 3D map of the patient’s spine, it involves the use of sophisticated imaging techniques, such as CT scans or intraoperative fluoroscopy, together with computerized navigation devices. By using this mapping, surgeons may more accurately and safely plan and carry out difficult spine surgeries.
The Benefits of Spinal Navigation:
- Enhanced Precision: With the use of spinal navigation devices, surgeons can see the patient’s spine in three dimensions in real-time and execute treatments with extreme precision. Better results and fewer problems may result from this accuracy.
- Minimized Radiation Exposure: By lowering the requirement for intraoperative X-rays, spinal navigation creates a safer surgical environment by reducing radiation exposure to the surgeon and OR staff.
- Optimized Surgical Planning: Surgeons can meticulously plan the procedure before making any incisions, ensuring minimal invasiveness and reduced tissue damage, ultimately leading to quicker recovery times.
- Real-time Feedback: These devices give the surgeon instant feedback and aid in preventing surgical errors by continuously tracking the surgical tools in relation to the anatomy of the patient.
- Versatility: Spinal navigation is a versatile tool for a wide range of patients and conditions. It can be used for a variety of spine treatments, such as spinal fusion, minimally invasive surgery, tumor excision, vertebroplasty, and difficult revision surgery.
Applications of Spinal Navigation:
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fractures, degenerative disc disease, and scoliosis are among the ailments that are frequently treated with this technique. The accurate placement of bone grafts and implants is ensured using spinal navigation.
- Complex Revision Surgery: Surgeons can more accurately navigate the altered anatomy and make the necessary modifications when using navigation to help patients who require revision surgery after a previous spinal operation fails.
- Implant Placement: Spinal navigation technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the precise and optimal placement of spinal implants.
- Deformity Correction: For conditions like scoliosis and kyphosis, spinal navigation assists in correcting spinal deformities with precision.
The primary benefit of spinal navigation is its capacity to give doctors better visualization and direction while performing surgery. Surgeons are better able to traverse the patient’s particular spinal anatomy by incorporating preoperative imaging data into the navigation system. The correct placing of spinal implants like screws, rods, or cages, as well as the reduction of problems, are made possible by real-time feedback and visualization. The precise bone removal, tumor removal, and alignment adjustments made possible by spinal navigation also contribute to better surgical outcomes and possibly quicker patient recoveries.


