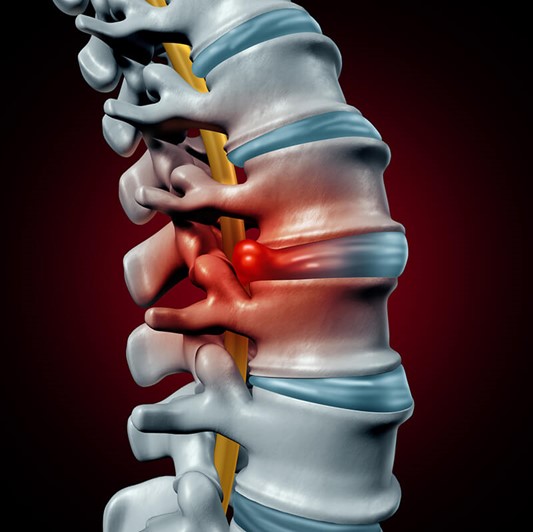
What is a Herniated Disc?
Often referred to as a “slipped disc,” a herniated disc is also known as a “bulged” or “ruptured” disc. Whatever the term used, one thing is for sure; it can be very painful and debilitating.
So, what exactly is a herniated disc? Your spine is made up of individual bones called vertebrae, and between each vertebra lies a disc, which acts as a cushion. These discs absorb shocks that are caused by everyday movements such as walking, running, twisting, and lifting.
There are two parts to a disc. The interior is made up of a soft, gelatinous-like material while the exterior ring is composed of a hard material. Due to spinal injury, deterioration, or weakness, the soft inside portion of the disc can protrude through the tough outer portion. This causes pain and discomfort, and if a nerve happens to be compressed, numbness along the nerve can also occur.
If you or someone you know is suffering from what may be a herniated disc, answers to some of the most commonly asked questions are listed below.
What Causes a Herniated Disc?
Most herniated discs are due to age but can also be from trauma, such as an injury lifting heavy objects, or a car accident. Over time, the tough ring surrounding the disc can become weakened, allowing the soft interior to slide out. This slippage can also occur from certain motions such as twisting and lifting. Lifting heavy objects puts a lot of pressure on the back and spine, and if not done correctly or there is weakness, the disc can become displaced. Similarly, if someone is very overweight, the added pressure on the spine can increase the risk of a herniated disc.
What Are the Symptoms of a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc can be very painful. Each person can experience this pain differently, depending on the location of the slipped disc (it can occur anywhere along the spinal column), and as mentioned, the slipped disc may compress a spinal nerve. Some of the most common symptoms of a herniated disc are listed below:
- pain and or numbness on one side of the body (most common)
- pain that spreads to your legs or arms
- pain that increases with particular movements or at night
- pain that gets worse after sitting or standing for a long period of time
- pain while going for short walks
- unidentifiable muscle weakness
- burning sensations, aching or tingling in the painful areas
How Do You Diagnose a Herniated Disc?
In order to determine if you have a herniated disk, you must visit a health professional. After performing a physical exam and investigating your medical history, they may order an imaging test. These may include x-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or myelograms.
What Are Common Treatments for a Herniated Disc?
Treatment for a herniated disc varies from person to person. It depends on the amount of pain, and if the slipped disc is affecting the surrounding nerves and muscles. Thankfully for most people, treatment includes over-the-counter pain medication and some at-home physical therapy. If your pain is more severe, your treatment plan may include prescription pain medications or muscle relaxers. Although uncommon, if after 6 weeks you are still experiencing pain, difficulty standing or walking, numbness or weakness, then other medical treatments or surgery may be required.
How Do You Prevent a Herniated Disc?
Although sometimes unavoidable, there are a few things you can do to decrease your risk of a herniated disc:
- practice good lifting techniques such as bending from your knees, not your waist
- maintain a proper weight in relation to your height
- exercise regularly and include workouts that strengthen your core and legs
- make sure to keep a good posture to avoid putting unnecessary strain on your back